






 Рейтинг: 4.2/5.0 (1906 проголосовавших)
Рейтинг: 4.2/5.0 (1906 проголосовавших)Категория: Windows: Расширения
 Ever have an application that just hangs and never returns to normal or terminate?
Ever have an application that just hangs and never returns to normal or terminate?
So you open up Windows Task Manager. find the application process, right click on it and select End Process.
You repeat the process. Nothing again. One more time…that process just won't terminate and die.
Well, having pesky processes, that refuse to terminate and continues to hog CPU cycles, can be frustrating to the point where you just want to hit the power button and shut down. But that's too risky and more times than not will cause loss of data or system boot problems.
What you need is a utility that can kill and terminate stubborn processes, the first time, using PsKill from Microsoft Sysinternals.
PsKill requires no installation and is a stand alone executable that is run from the command line. It can kill process locally or remotely. PsKill is bundled with Sysinternals PsTools which is a collection of command line tools for Windows computers.
To use PsKill, you want to get things setup first:
If it is not visible, click on View \ Select Columns… and make sure PID (Process Identifier) is checked and select OK.
(just substitute 1680 with your PID number that you want terminated).
The process WILL terminate freeing your computer from application hell.
You should be able to re-open the application again. But be careful, killing processes this way may cause data loss with the application that was terminated (such as if you were using a text editor or Microsoft Word).
At least you won't have to reboot ![]()

Как другие пользователи поступают с этим файлом?
Всего голосов (2 ), 1 говорят, что не будут удалять, а 1 говорят, что удалят его с компьютера.
процесс kill.cmdпапка: c:\users\samsung\desktop\antiwinblock 2.9.9 win8.1pe\antiwinblock_iso\awbl\programs\dr.web\prog\kill.cmd частью: unknown product компания: unknown company Версия продукта: размер: 249 MD5= d919d1fcc539559ce29e5e51d2501ad8
папка: c:\drweb\kill.cmd частью: unknown product компания: unknown company Версия продукта: размер: 243 MD5= aa6ca4ce7f96f58f5f3bca28fdd04041
папка: c:windowskm$minikill.cmd частью: unknown product компания: unknown company Версия продукта: размер: 376 MD5= b7d06ce2bdc2de2fcfdc62e8ca297967
папка: c:lop sdkill.cmd частью: unknown product компания: unknown company Версия продукта: размер: 11189 MD5= b97a1ada3d830e075c9c2238ab02379a
папка: c:program filesinternet download managerkill.cmd частью: unknown product компания: unknown company Версия продукта: размер: 424 MD5= 0a3573c1e76f32e1383e2c481d33bc4d
папка: c:intalador de windowswindows7pointprogsoftyahookill.cmd частью: unknown product компания: unknown company Версия продукта: размер: 66 MD5= 13ebd7561027892ee558c3f70e3b34f7
папка: c:intalador de windowswindows7pointprogsoftgooglecrokill.cmd частью: unknown product компания: unknown company Версия продукта: размер: 58 MD5= 990583441ab910fe6528b1bee66e9500
папка: d:\. \. \. \Googletalk\kill.cmd частью: unknown product компания: unknown company Версия продукта: размер: 35 MD5= 65a7786b73e2549d9307fca99dbc8f62
папка: d:\. \. \. \Yahoo\kill.cmd частью: unknown product компания: unknown company Версия продукта: размер: 54 MD5= 12bf3af8498c409e7d0ee2f46cb978a9
 скачать бесплатно Dr Prot Antivirus
скачать бесплатно Dr Prot Antivirus
A more flexible way to kill processes interactively is the zap shell script, presented by Brian Kernighan and Rob Pike in their classic book The UNIX Programming Environment. The script uses egrep (Section 13.4 ) to pick the processes to kill; you can type extended expressions (Section 32.15 ) that match more than one process. The expressions can match partial or complete command names, any arguments to the commands, or, actually, any part of the command's line in the ps output. For example:
We reprint the script by permission of the authors:
 Go to http://examples.oreilly.com/upt3 for more information on: zap
Go to http://examples.oreilly.com/upt3 for more information on: zap
The ps -ag command displays all processes on the system. Leave off the a to get just your processes. Your version of ps may need different options (Section 24.5 ).
This shell version of zap calls another script, pick. shown below.[75] pick shows each of its command-line arguments and waits for you to type y. q. or anything else. Answering y writes the line to standard output, answering q aborts pick without showing more lines, and any other answer shows the next input line without printing the current one. zap uses awk (Section 20.10 ) to print the first argument (the process ID number) from any ps line you've selected with pick. The inner set of nested (Section 36.24 ) backquotes (Section 28.14 ) in zap pass pick the output of ps. filtered through egrep. Because the zap script has set the IFS variable (Section 36.23 ) to just a newline, pick gets and displays each line of ps output as a single argument. The outer set of backquotes passes kill (Section 24.12 ) the output of pick. filtered through awk.
[75]The MH email system also has a command named pick. If you use MH, or frontends like exmh or mh-e, you could rename this script to something like choose .
If you're interested in shell programming and that explanation wasn't detailed enough, take a careful look at the scripts -- they're really worth studying. (This book's shell programming chapters, 44 through 46, may help, too.) Here's the pick script:
 Go to http://examples.oreilly.com/upt3 for more information on: pick
Go to http://examples.oreilly.com/upt3 for more information on: pick
Our customer has some Windows 2003 servers running batch jobs activated by Task Scheduler. The actual programs performing the work are custom .exe processes, and they are aggregated into .cmd scripts so that they get launched together by Task Scheduler when the scheduled interval comes by. The lines within the cmd scripts may or may not use the Call command to launch the separate .exe programs.
In this setup, Task Scheduler is effectively monitoring cmd.exe, and when using Process Explorer, one can observe that the child .exe processes are parked under the cmd.exe process tree. However, when Task Scheduler kills cmd.exe due to exceeding the permissible time limit, the child .exe processes may not be killed along with their parent and become orphaned. Those processes remain stalled indefinitely. Due to the state of the process threads shown in Process Explorer, i suspect those processes end up in error and popped up a .NET debugger dialog box (these are .NET applications) which cannot be seen since the batch job user is a separate user account.
Initially when i was investigating this behaviour on my Windows XP workstation, I observed that child .exe processes launch from my test .cmd script do get killed together with the cmd.exe when Task Scheduler decides time is up. There was no way I could orphan the child processes.
Based on a hunch, i eventually moved over to a Windows 2003 machine to test this. Similarly, the child processes to get terminated like those in my workstation. My second step was then to use another user account to run the scheduled task. This time round, cmd.exe gets killed after the time limit is exceeded, but the child processes remain standing, just like what my customer observed in their production servers.
If i preemptively logon that batch user account (which just so happened to be another admin account) to claim a desktop session, any error or info pop-ups from my test .exe programs would be routed and rendered on that desktop, allowing me to see the actual user output. If i only logon after the scheduled task had been invoked, the desktop session will not "reclaim" the existing processes' windows; they stay hidden forever.
My question is, what condition(s) am I missing here that can cause Task Scheduler not to wipe out the child processes under a cmd.exe? What is special about using another account that would induce this behaviour, but not when using my current administrator account to run the schedued task?
Occasionally in Mac OS X, it may be necessary to force a program or process to quit. For example, if a particular program fails to respond or unexpectedly hangs. Every application on a Mac comprises of one or more processes.
It’s usually possible to use the Force Quit command (?? esc) in the Apple Menu. but only individual applications are listed in the Force Quit Applications window rather than all processes which are running on your computer.
The Force Quit Applications Pop-up
The basic steps to check and kill a process are:
Each step is described in more detail below.
About TerminalProbably the most useful tool to check and kill processes is called Terminal. which is an application that provides access to the lower levels of the Mac OS X operating system and files. Terminal is a text-based tool which lets you conduct all manner of routine tasks such as viewing directories, copying, moving and deleting files, as well as obtain detailed information about each process running including:
A related indispensable application is Activity Monitor – a graphical tool that allows you to manage processes, however it doesn’t have quite the same capabilities that Terminal does. Activity Monitor shows common process-related details such as the memory used and percentage of CPU that each process is consuming. When used together, Activity Monitor and Terminal provide a powerful yet relatively straightforward way to inspect and manage wayward processes.
The main Activity Monitor window is shown below.
Each application on your Mac has an associated Process ID (a PID) and a user-friendly name. From here you can inspect or quit each process, but in this example we use Activity Monitor simply as a companion to Terminal.
The Apple Mail application is displayed in Activity Monitor with a PID number of 14649. Note that process ID’s are assigned by Mac OS, and therefore will not be the same on your computer as somebody else’s.
The Activity Monitor Application
How to Use TerminalThe first step is to open Terminal either from the Applications -> Utilities folder or simply type Terminal into Spotlight. Terminal is always represented by the icon below.
Once it opens you’ll be presented with a standard Terminal window as below.
The first line shows the date and time when you last logged in. The second line is the command prompt which is where you enter the commands you wish to execute. The command prompt always begins with your computer name followed by your local Account Name.
The current directory (the “working directory”) when you open Terminal always defaults to your Home Folder.
Basic Terminal CommandsBefore we describe how to check and terminate a process on your computer it’s worth knowing a few basic Terminal commands.
Note that many commands in Terminal can accept various options (sometimes called switches) that can alter their effect. The simplest way to discover the available command-line options is to type the command into Terminal followed by -? such as ls -?
Another useful command is apropos. Enter apropos <command> into the Terminal window for a description of that command and its options.
To View All Processes Running Processes Displayed
Running Processes Displayed
The process list displayed using ps -ax may include a hundred or more processes, but it’s quite simple to identify a process based on the name in the CMD column (for example Skype is listed as /Applications/Skype.app/Contents/MacOS/Skype), or even by the PID if you already know it.
As shown in Activity Monitor earlier, the Mail application on my Mac had the PID 14649, so it’s simple to scroll down the Terminal window until the relevant process is found.
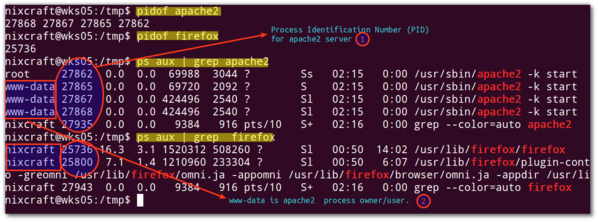
One very useful command to help find a process by name or PID is grep which can filter out the desired information. It can be used in conjunction with the ps -ax command to list only the process that you are interested in.
For example:
The “pipe” function (“|”) simply uses the output from the process list as an input to grep, to filter out the desired process name.
Assuming that Skype is actually running, you may see a result something like this:
Roland-Bankss-MacBook-Pro:
roly$ ps -ax | grep Skype 14530. 0:56.32 /Applications/Skype.app/Contents/MacOS/Skype -psn_0_9218250 14947 ttys000 0:00.00 grep Skype
This example shows that Skype has a PID of 14530 and also the folder where Skype was launched from. The last line is just the process ID of the grep command itself, which can be safely ignored.
Repeating the command with the Skype process ID instead i.e. ps -ax | grep Skype yields the same result.
To Terminate (Kill) a ProcessOnce you know the process ID, killing it using Terminal is very simple. Be cautious however because forcing a process to suddenly exit can have unforeseen consequences, so it’s advisable to check carefully that the process you are about to kill is the correct one. There are essentially two easy ways to kill a process:
Caution: killall should be used sparingly to avoid accidentally terminating the wrong processes. There is no confirmation prompt to ask if you really do wish to kill the processes, so check carefully beforehand
![]() 16-04-2011, 08:16 AM
16-04-2011, 08:16 AM
I found this in one of the best tweak guides sites,in my point of view it helps when u have a virus and your taskmanager doesn't respond.
All of this is possible with the TaskKill command. First, let's cover the basics. You can kill a process by the process ID (PID) or by image name (EXE filename).
Open up an Administrative level Command Prompt and run tasklist to see all of the running processes:
C:\>tasklist
Image Name PID Session Name Mem Usage
========================= ======== ================ ============
firefox.exe 26356 Console 139,352 K
regedit.exe 24244 Console 9,768 K
cmd.exe 18664 Console 2,380 K
conhost.exe 2528 Console 7,852 K
notepad.exe 17364 Console 7,892 K
notepad.exe 24696 Console 22,028 K
notepad.exe 25304 Console 5,852 K
explorer.exe 2864 Console 72,232 K
In the example above you can see the image name and the PID for each process. If you want to kill the firefox process run:
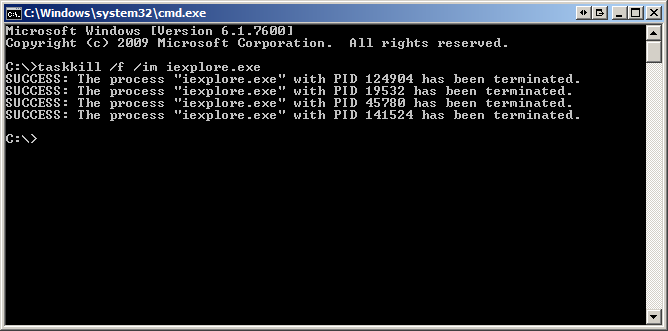
C:\>Taskkill /IM firefox.exe /F
C:\>Taskkill /PID 26356 /F
The /f flag is kills the process forcefully. Failure to use the /F flag will result in nothing happening in some cases. One example is whenever I want to kill the explorer.exe process I have to use the /F flag or else the process just does not terminate.
If you have multiple instances of an image open such as multiple firefox.exe processes, running the taskkill /IM firefox.exe command will kill all instances. When you specify the PID only the specific instane of firefox will be terminated.
The real power of taskkill are the filtering options that allow you to use the following variables and operators.
Программа kill используется для управления работающими процессами по их PID, с помощью отправки им управляющих сигналов.
Пользователь root, может управлять любыми процессами, в том числе и процессами других пользователей. Если не указано символическое имя или номер сигнала, отправляется сигнал TERM .
Возможны следующие опции:
-s имя_сигнала
Данная опция позволяет отправить сигнал процессу, используя его символическое имя. По-умолчанию отправляется сигнал TERM. На самом деле, эту опцию можно опускать, устанавливая только знак "- " перед именем или номером сигнала, например: -HUP или -1 .
-l [код_завершения] Без указания операнда, выведет имена сигналов. Иначе, покажет имя сигнала, соответствующего указанному коду_завершения. -имя_сигнала Указать символическое имя сигнала, для отправки процессу. -номер_сигнала Указать сигнал по его числовому значению ( только положительное число )
Следующие PID имеют специальное значение.
-1 При выполнении пользователем root, отправляет сигнал всем процессам, иначе всем процессам принадлежащим данному пользователю.
Ниже представлены самые часто-используемые сигналы, имеет смысл, запомнить их:
Некоторые системные оболочки имеют встроенную команду kill с идентичным или похожим функционалом. За дополнительной информацией обратитесь к справочному руководству man buildin .
При успешном завершении, программа kill. возвращает 0. иначе >0 .
Примеры использования:
Многие демоны, реагируют на сигнал HUP, перечитыванием конфигурационного файла, без прерывания работы. Напрмер, у нас работает некий демон с PID 123. мы, не прерывая его работы, вносим изменения в конфигурационный файл. Что-бы работающий демон принял эти изменения, отправляем ему сигнал HUP .
Что-бы безусловно завершить процесс ( например в случае его зависания ), используем сигнал KILL. или 9 в числовом эквиваленте. Сигнал KILL не перехватывается, уничтожение процесса происходит на уровне операционной системы .
Кроме того можно управлять группой процессов по их PGID :
Смотри так-же:
builtin(1), csh(1), killall(1), ps(1), kill(2), sigaction(2)
What would be the command to kill a process like explorer.exe or wininit.exe through cmd?
Enable System Protection on Local Disk (C:) with CMD
location: 7forums.com - date: January 16, 2013
Hello. I Have a Netbook Windosw Home Premium 64bit (no CD Drive). After an Windows Update I can't boot anymore. By searching google I found a lot of posts with the same problem, with or without solutions that worked for these people. Unfortunately non worked for me. Can you please show me how to enable System Protection vy using CMD for C:\ so i can do a System Restore? Thank you very much for your future efforts! Best Regards Vincent
Hi, I'm new to this "deep computer knowledge", so I was thinking maybe you guys could help me with this question. By the way, I'm sorry if this question has already been asked! So, to the question; My friend said that he gave his Win8 Pro (as an upgrade version) version to his little brother but said he reset the activation key via cmd so his brother could use it again and not buy his own key. He said he did the resetting by typing in slmgr/upk, slmgr/cpky and slmgr/rearm (or what it is) so the key would work as a new one. But is it just that simple? What I know, you can only use the Win8 Pro key once, and if you install Win8 Pro on a new computer you have to buy a new key. He only put his computer to a
Anyone out there knows if it's possible to enable/disable (turn on/turn off) Airplane Mode either using CMD or with two separated shortcuts (i.e. desktop shortcut 1 enables Airplane Mode, desktop shortcut 2 disables Airplane Mode)?
Anyone out there knows if it's possible to enable/disable (turn on/turn off) Airplane Mode either using CMD or with two separated shortcuts (i.e. desktop shortcut 1 enables Airplane Mode, desktop shortcut 2 disables Airplane Mode)?
I would like to know how to remove Windows.old with cmd prompt. What are the three lines of code that would do this.
Now, the title might sound like thats whats meant to happen, but whenever I open a .bat file it just launches the regular command prompt. This all happened when I went to the "Associate a file extention with a program" section of Control Panel and set .bat files to launch with C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exe. Can anyone help? Thanks, techhead287
I'm following the instructions here, but adding the step of moving the Programs (x86) folder as well, since my computer is 64-bit. Every-time I try, says access denied whether or not I run it as a admin or am owner of said folder. I've also tried doing this in the cmd prompt of the system recovery cd. Any help would be appreciated.
When I first installed Windows 7 I used Process Explorer to pick through all of my services, learning what they were, clicking on search and reading the Google results. I got to the point where I could just look them over every day or so and make sure nothing unwanted was running. Lately I tried searching and it opens Wikipedia instead of Google. I looked at options and everywhere else I could think of and I don't see where to change this option. Can anyone help me out? Thanks, Rusty